Introduction

Canine infectious diseases can pose a serious threat to the health and well-being of our beloved four-legged companions. Understanding these diseases and taking preventive measures is crucial in protecting our dogs from potential harm.
Importance of understanding canine infectious diseases

Understanding canine infectious diseases is crucial for dog owners because it allows them to protect and safeguard the health of their beloved pets. By gaining knowledge about these diseases, owners can take necessary preventive measures and ensure that their dogs receive appropriate medical care when needed. This understanding also empowers owners to recognize the signs and symptoms of infectious diseases early on, enabling swift intervention and better outcomes for their dogs' well-being.
The role of prevention in maintaining dog's health

Prevention plays a crucial role in maintaining a dog's health by minimizing the risk of infectious diseases. Regular vaccinations, proper hygiene practices, and preventative medications help safeguard dogs against harmful pathogens. By focusing on prevention, dog owners can promote their pet's overall well-being and prevent the onset of potentially dangerous illnesses.
Common Canine Infectious Diseases

Common canine infectious diseases are a significant concern for dog owners and can have serious consequences for their pets' health. These diseases, which can be caused by viruses, bacteria, parasites, or fungi, can spread easily and lead to various symptoms and health complications. It is essential for dog owners to be aware of these commonly encountered infectious diseases to protect their furry friends and take appropriate preventive measures.
Parvovirus and its symptoms

Parvovirus is a highly contagious viral infection that affects dogs, especially puppies. The virus primarily targets the gastrointestinal tract and can cause severe symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea (often bloody), lethargy, loss of appetite, and dehydration. Puppies infected with parvovirus are more susceptible to complications and may require intensive veterinary care to survive. Early detection and prompt treatment are essential in managing this potentially fatal disease.
Distemper and its transmission
Distemper is a highly contagious viral disease that affects dogs. It is primarily transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or exposure to their bodily fluids, such as urine, saliva, or nasal discharge. The virus can also be spread through contaminated objects or surfaces.
The transmission of distemper can occur through various routes, including close proximity to infected animals, sharing food and water bowls, and even through respiratory droplets expelled by infected dogs. Puppies and unvaccinated dogs are particularly susceptible to contracting distemper.
Once an infection occurs, the virus targets the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems of the dog. It can cause symptoms such as fever, coughing, diarrhea, nasal discharge, loss of appetite, and neurological signs like seizures and muscle twitching.
Efforts should be made to prevent the transmission of distemper by vaccinating puppies and adult dogs according to the recommended vaccination schedule. Isolating infected animals and practicing good hygiene measures are also essential in preventing the spread of this debilitating disease.
By understanding how distemper is transmitted and taking appropriate preventive measures, dog owners can protect their pets from this dangerous viral infection.
Viral Infections

Viral infections are a common health concern for dogs and can have serious consequences if not properly addressed.
Canine hepatitis and its prevention

Canine hepatitis is a viral infection that affects the liver of dogs and can lead to serious health complications. The main cause of canine hepatitis is the Canine Adenovirus Type-1 (CAV-1). Thankfully, there are effective measures available for preventing this disease and keeping our furry friends safe.
Prevention is crucial when it comes to canine hepatitis. The most effective way to prevent this disease is through vaccination. The canine adenovirus vaccine, commonly known as the DHPP vaccine, includes protection against CAV-2, a closely related virus that provides cross-immunity against CAV-1.
Puppies should receive their first vaccination against canine hepatitis at around 8 weeks of age, followed by boosters at 12 and 16 weeks. Adult dogs should receive regular booster shots every one to three years, depending on their individual risk factors.
Apart from vaccination, maintaining good hygiene practices is also essential in preventing the spread of canine hepatitis. Dog owners should ensure that their pets have access to clean water and food, as contaminated sources can increase the risk of infection. Additionally, avoiding contact with infected dogs or their bodily fluids can help prevent transmission.
By staying proactive and taking preventive measures such as vaccination and practicing good hygiene, we can significantly reduce the risk of our beloved dogs contracting canine hepatitis. Consulting with a veterinarian about vaccination schedules and other preventive strategies will ensure that we are providing the best possible care for our furry companions.
Canine influenza and vaccination

Canine influenza, also known as dog flu, is a contagious respiratory disease that affects dogs. It is caused by the influenza Type A virus. Just like humans, dogs can get infected with different strains of the flu virus. Canine influenza can spread easily among dogs through nasal secretions and respiratory droplets.
Vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing canine influenza. Vaccines are available to protect against both strains of the flu virus - H3N8 and H3N2. These vaccines can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms if a dog does contract the virus.
It is recommended to vaccinate dogs that are at a higher risk of exposure, such as those who frequently interact with other dogs in places like boarding facilities, daycare centers, or dog parks. Puppies, senior dogs, and dogs with underlying health conditions should also be vaccinated.
Vaccination for canine influenza typically involves an initial series of two shots given two to four weeks apart, followed by annual booster shots. It's important to consult with your veterinarian to determine the most appropriate vaccination schedule for your dog based on their individual needs and risk factors.
In addition to vaccination, practicing good hygiene can further minimize the risk of canine influenza transmission. Avoid exposing sick dogs to healthy ones and follow proper handwashing protocols after handling multiple dogs or coming into contact with potentially contaminated objects or surfaces.
By being proactive and ensuring your dog receives appropriate vaccinations for canine influenza, you can help protect their health and reduce the spread of this infectious disease among canine communities.
Bacterial Infections

Bacterial infections are a common type of canine infectious disease that can cause various health issues in dogs. These infections are caused by harmful bacteria that enter the dog's body and multiply, leading to illness. It is important for dog owners to understand bacterial infections and take necessary steps for prevention.
Lyme disease and tick prevention
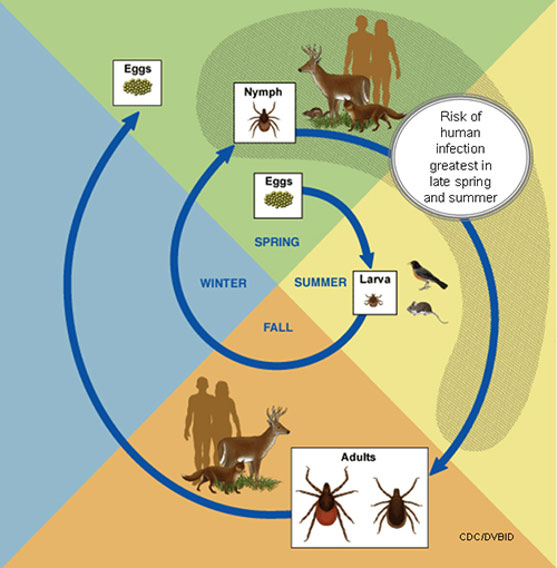
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection transmitted to dogs through the bite of infected ticks. It is important for dog owners to be aware of Lyme disease and take proactive measures to prevent tick infestations on their pets. Tick prevention is crucial in reducing the risk of Lyme disease and other tick-borne illnesses. Regularly checking your dog for ticks, especially after outdoor activities, is essential. Using tick control products such as collars, sprays, or spot-on treatments can also help prevent tick infestations. Additionally, keeping your yard clean and free from tall grasses or leaf piles can minimize the tick population in your surroundings. By taking these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the chances of your dog contracting Lyme disease and protect their overall health and well-being.
Leptospirosis and its transmission
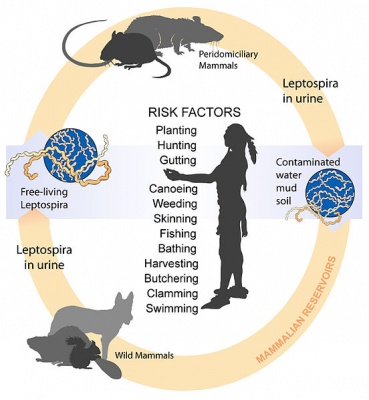
Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection caused by the Leptospira bacteria and it can affect both dogs and humans. The bacteria are commonly found in soil and water, especially in areas with warm and humid climates. Dogs can become infected with Leptospirosis through direct contact with the urine of infected animals or by drinking water that has been contaminated with the bacteria. The bacteria can enter the dog's body through cuts or wounds on their skin, or through mucous membranes such as the eyes, nose, or mouth. It is important to prevent exposure to contaminated environments and ensure that your dog's vaccinations are up to date to protect against this dangerous disease.
Parasitic Infections

Parasitic infections are common among dogs and can have a significant impact on their health and well-being. These infections are typically caused by parasites such as heartworms, fleas, and ticks. It is essential for dog owners to understand the dangers associated with these parasites and take preventive measures to protect their furry friends.
Heartworm disease and prevention
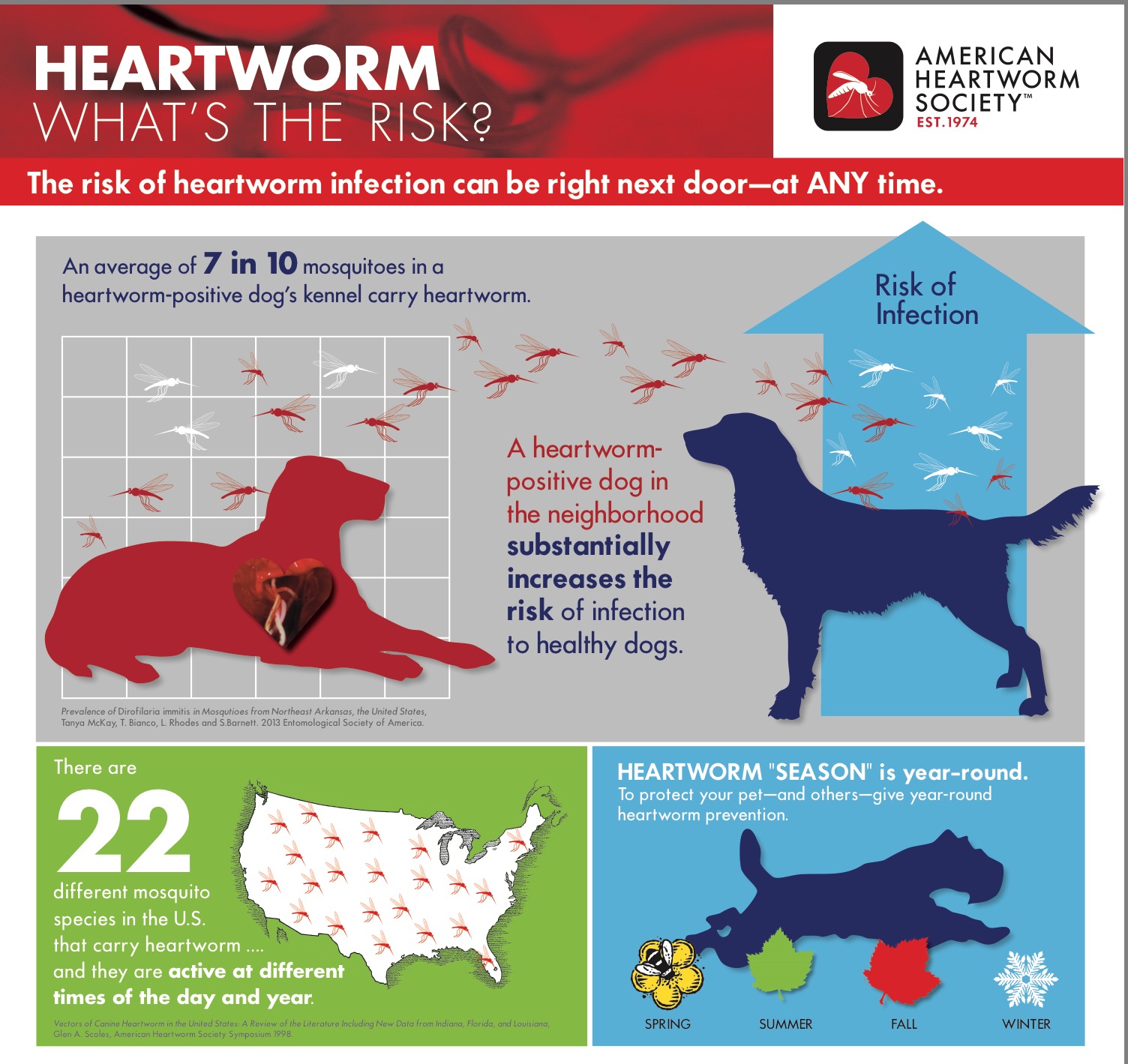
Heartworm disease is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that can affect dogs. It is caused by the parasitic worm Dirofilaria immitis, which is transmitted through mosquito bites. Once inside the dog's body, the worms mature and reside in the heart, lungs, and blood vessels, causing damage and adversely affecting the dog's overall health.
Prevention is essential in protecting dogs from heartworm disease. Thankfully, there are several preventive measures available. The most common method is through the administration of monthly oral or topical medications specifically designed to kill heartworm larvae and prevent their further development in the dog's body. These preventive treatments should be started when the dog is young and continued throughout their life.
Additionally, minimizing exposure to mosquitoes can help reduce the risk of heartworm infection. This can be achieved by keeping dogs indoors during peak mosquito activity times, using insect repellents specifically formulated for dogs, and eliminating standing water around the house where mosquitoes breed.
Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for monitoring a dog's heartworm status. Veterinarians often recommend annual heartworm testing to ensure early detection and prompt treatment if necessary. In areas where heartworm disease is prevalent, some veterinarians may suggest more frequent testing to ensure optimal protection.
By understanding the risks associated with heartworm disease and following preventive measures consistently, dog owners can effectively safeguard their pets from this debilitating condition. As with any infectious disease prevention strategy, it is always best to consult with a veterinarian who can provide personalized advice based on a dog's specific needs.
Fleas and ticks prevention
Fleas and ticks prevention is crucial in safeguarding your dog's health. Regularly administer flea and tick treatments, use preventive medications, and regularly inspect your dog for signs of infestation. Keep your dog's environment clean and avoid areas with high flea and tick populations to minimize the risk of infection.
Fungal Infections

Fungal infections are another common type of infectious disease that can affect dogs. These infections are caused by various types of fungi, such as ringworm and blastomycosis. Fungal infections can cause a range of symptoms, including skin lesions, hair loss, itching, and respiratory issues. Treatment for fungal infections typically involves antifungal medication and proper hygiene practices to prevent the spread of the infection to other pets or humans. It is important for dog owners to be aware of the signs of fungal infections and take appropriate measures to prevent and treat them.
Ringworm and its treatment
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that can affect dogs. It is not caused by worms, but rather by a type of fungus called dermatophytes. The infection gets its name from the distinctive ring-shaped rash that often appears on the affected area.
When it comes to treating ringworm in dogs, there are several options available. One of the most common treatments is the use of antifungal medications, either in the form of topical creams or oral medication. These medications work by eliminating the fungus and preventing its spread to other parts of the body.
In addition to medication, it is important to practice good hygiene and regularly clean and disinfect any surfaces or items that may have come into contact with the infected dog. This includes bedding, toys, and grooming tools.
In some cases, if the infection is severe or does not respond to traditional treatments, your veterinarian may recommend additional measures such as medicated baths or shaving the affected area to allow for better penetration of the antifungal medication.
It is crucial to follow your veterinarian's instructions carefully and complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve. This will help ensure that the infection is completely eradicated and does not return.
If you suspect that your dog may have ringworm, it is important to consult with your veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. They will be able to guide you through the process and provide necessary support for your dog's recovery.
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are key in effectively managing ringworm infections in dogs. By taking proactive measures and following proper treatment protocols, you can help your furry friend overcome this fungal infection and prevent its recurrence.
Blastomycosis and its symptoms
Blastomycosis is a fungal infection caused by the organism Blastomyces dermatitidis. This infection primarily affects dogs and humans who are exposed to contaminated soil. The symptoms of blastomycosis in dogs can vary but commonly include fever, coughing, difficulty breathing, weight loss, lethargy, and skin lesions. If left untreated, blastomycosis can lead to severe respiratory distress and even death. It is important for dog owners to be aware of these symptoms and seek veterinary care if they suspect their dog may be infected with blastomycosis.
Prevention Strategies

Prevention strategies are crucial in safeguarding the health of our canine companions. By implementing effective practices, we can decrease the risk of them contracting infectious diseases. These strategies involve vaccination schedules for puppies and adult dogs as well as maintaining proper hygiene practices.
Vaccination schedule for puppies and adult dogs

Vaccination is a crucial aspect of preventing canine infectious diseases in both puppies and adult dogs. It is important to follow a proper vaccination schedule recommended by veterinarians.
Proper hygiene practices
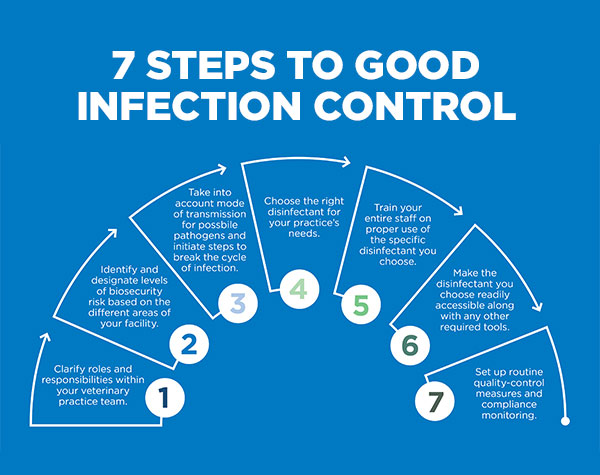
Proper hygiene practices are essential in preventing the spread of canine infectious diseases. Keeping your dog's living area clean and following proper sanitation protocols can greatly reduce the risk of infection. This includes regularly cleaning and disinfecting their bedding, toys, and food bowls. Additionally, practicing good hand hygiene by washing your hands thoroughly after handling your dog or cleaning up after them is crucial. Maintaining a clean environment not only protects your dog from potential pathogens but also prevents them from spreading diseases to other animals and humans. By incorporating proper hygiene practices into your daily routine, you can help ensure the health and well-being of your canine companion.
Early Detection and Diagnosis

Early detection and diagnosis of canine infectious diseases play a crucial role in ensuring the health and well-being of our furry friends. By recognizing the signs and symptoms early on, we can take necessary actions to prevent the spread of the disease and provide appropriate treatment. Regular check-ups and tests are essential for identifying any potential infections or underlying health issues.
Signs and symptoms of canine infectious diseases
Canine infectious diseases can manifest themselves in various ways, and it is essential for pet owners to be aware of the signs and symptoms. Common indicators include fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, coughing, sneezing, vomiting, diarrhea, skin infections, and abnormal behavior. These symptoms can vary depending on the specific disease and its severity. It is crucial to monitor your dog's health closely and seek veterinary attention if you notice any of these signs. Early detection plays a vital role in the successful treatment and prevention of further spread of infectious diseases.
Importance of regular check-ups and tests

Regular check-ups and tests are vital in maintaining the health and wellbeing of our dogs. These routine examinations allow veterinarians to detect any potential issues early on, enabling prompt treatment and prevention of further complications. Through regular check-ups and tests, veterinarians can assess the overall health of the dog, monitor vaccinations, and screen for any underlying conditions or infectious diseases. Additionally, these visits provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns or behavioral changes observed in our furry companions. By prioritizing regular check-ups and tests, we can ensure that our dogs receive the necessary care they need to lead happy and healthy lives.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding and preventing canine infectious diseases is crucial for maintaining a dog's health and well-being. By following proper hygiene practices, staying up-to-date with vaccinations, and being vigilant for early signs and symptoms, dog owners can help protect their furry friends from these potentially serious illnesses. Regular check-ups and tests are also important in detecting diseases early on. For more information and assistance, there are many resources available to provide guidance on preventing and managing canine infectious diseases.
Key takeaways on understanding canine infectious diseases and prevention
Understanding canine infectious diseases is crucial for dog owners to ensure the health and well-being of their pets. By staying informed about common illnesses such as parvovirus and distemper, owners can recognize the symptoms and seek prompt treatment. Vaccinating dogs against viral infections like canine hepatitis and influenza plays a pivotal role in preventing these diseases. Additionally, practicing proper tick prevention measures can safeguard dogs from bacterial infections like Lyme disease and leptospirosis. Preventing parasitic infestations, such as heartworm disease and fleas, requires regular preventive treatments. Familiarity with fungal infections like ringworm and blastomycosis helps owners identify symptoms and seek appropriate treatment. Understanding prevention strategies like vaccination schedules and hygiene practices ensures the overall health and wellness of dogs. Regular check-ups and diagnostic tests help detect infections early, allowing for prompt intervention. By following these key takeaways, dog owners can actively protect their beloved pets from infectious diseases and maintain their overall well-being.
Resources for further information and assistance

There are various resources available to provide further information and assistance regarding understanding canine infectious diseases and prevention. Pet owners can consult their veterinarians who can offer expert advice tailored to their dog's specific needs. Additionally, reputable websites, such as the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), can provide comprehensive information on various canine infectious diseases and prevention strategies. It is important to rely on reliable sources for accurate and up-to-date information.




0 Comments